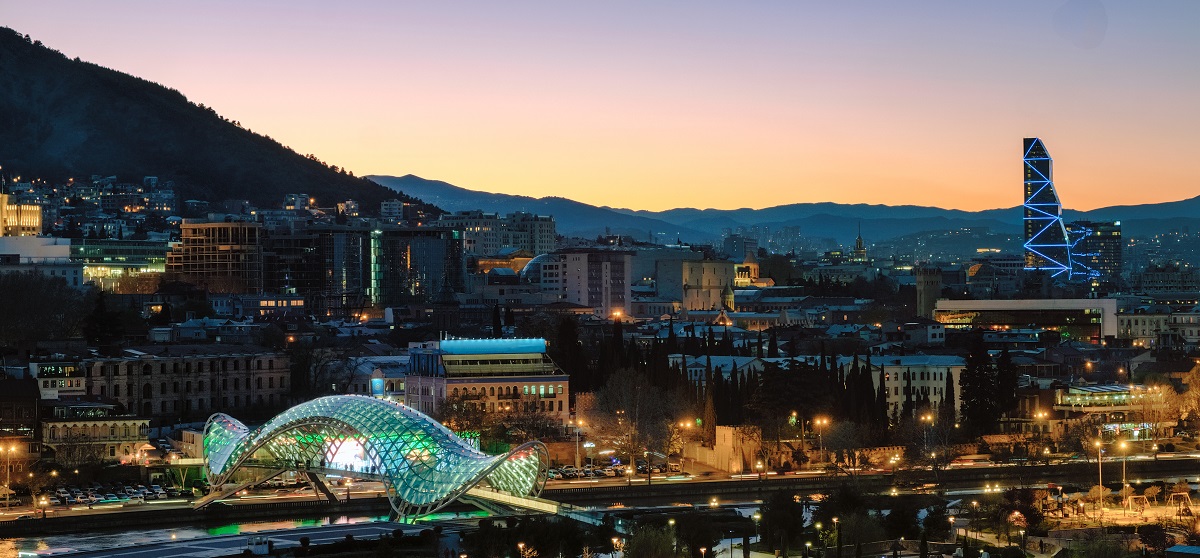
What most people know about Georgia is that it has a long and proud history of winemaking. What people don’t know about the country of Georgia is that it sustains a business-friendly environment through flexible, thorough, supportive and far-reaching legislation.
In 2014, the EU and Georgia signed a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Agreement (DCFTA) that guaranteed Georgia to be an inseparable part of the common market of European Union making the country very welcoming towards investors, encouraging foreign investment. Legislation supervising foreign investment has created appealing conditions giving foreign investors the same privileges and rights to locals.
So, what are the things that you should know about?
Starting a business in Georgia
According to the World Bank Ease of Doing Business 2020 Data, Georgia ranks 7th in the list of countries that’s easy to conduct business. It only takes a day or two to register a business and the fair is quite low, ranging from 40-60 USD.
As for the rules concerning reorganizations, more information can be found in The Law of Georgia for Entrepreneurs.
Taxes
Tax and customs legislation is merged under a single tax code and is collected and supervised by the Revenue Service of Georgia. So, there is Corporate Profit Tax (15%), Value Added Tax (18%), Personal Income Tax (20%), Import Tax (0-12%), Excise Tax (on selected goods) and Property Tax (stopping at 1%).
Permits, Certificates, Licenses
To-be-established companies that are going to have an impact on the environment, human life or health, are obliged to prepare an essential check called Environmental Impact Assessment and subsequently, present it to the Ministry of Environment Protection and Agriculture.
Trade and Customs
Customs procedures in Georgia are pretty transparent and take no longer than 15-20 minutes. Taking into consideration the fact that Georgia has free trade agreement with Ukraine, Turkey, China, including EFTA and CIS countries, on top of the DCFTA with the EU, without imposing customs or import rates, Georgian goods are available to roughly 2.5 billion population markets.
Data Protection Laws
The Law of Georgia about data protection aims to secure human rights and freedoms, including privacy if the personal data has to be mined. The law applies in these following cases: Automatic data processing, Semi-automatic data processing, Non-automatic data processing inside Georgia. The principles of data processing encompasses rules like data being processed for only the amount of time that is needed to process the data, without damaging subjects’ dignity, collected data, if not necessary or relevant, must be deleted, destroyed or stored in a way that guarantees anonymity of the person.
In conclusion, Georgia is definitely open to foreigners and is ready to accommodate. Taking into consideration the tireless refinement and updating of the business environment it is definitely on the rise of becoming a reliable investment destination in Eurasia.